Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

उत्तर
(a) 5a + T − 5g = 0
From free-body diagram (1),
T = 5g − 5a .....(i)
Again,
\[\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)T - 4g - 8a = 0\]
⇒ T − 8g − 16a = 0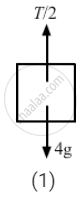
From free-body diagram (2),
T = 8g + 16a ......(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii), we get:
5g − 5a = 8g + 16a
\[\Rightarrow 21a = - 3g - a = - \frac{9}{7}\]
So, the acceleration of the 5 kg mass is \[\frac{9}{7} m/ s^2 \left(\text{ upward }\right)\] and that of the 4 kg mass is
\[2a = \frac{2g}{7} \left(\text{ downward }\right)\]
\[4a - \frac{T}{2} = 0\]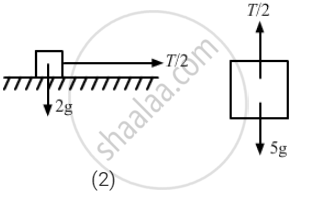
⇒ 8a − T = 0
⇒ T = 8a
Again, T + 5a − 5g = 0
From free body diagram-4,
8a + 5a − 5g = s0
⇒ 13a − 5g = 0
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{5g}{13} \left(\text{ downward }\right)\]
Acceleration of mass 2 kg is \[2a = \frac{10}{13} \left( g \right)\] and 5 kg is
\[\frac{5g}{13}\].
(c) T + 1a − 1g = 0
From free body diagram-5
T = 1g − 1a .....(i)
Again, from free body diagram-6,
\[\frac{T}{2} - 2g - 4a = 0\]
⇒ T − 4g − 8a = 0 .....(ii)
From equation (i)
1g − 1a − 4g − 8a = 0
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{g}{3}\left(\text{ downward }\right)\]
Acceleration of mass 1 kg is \[\frac{g}{3} \left(\text{ upward }\right)\]
Acceleration of mass 2 kg is \[\frac{2g}{3} \left(\text{ downward }\right)\] 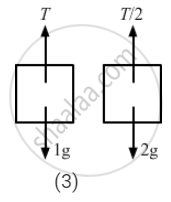
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms–1. How long does the body take to stop?
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
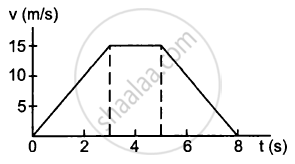
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
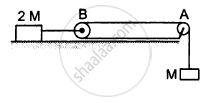
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
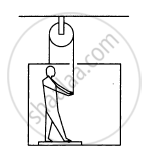
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
Why does a child feel more pain when she falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
