Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
उत्तर
Given,
m1 = 100 g = 0.1 kg
m2 = 500 g = 0.5 kg
m3 = 50 g = 0.05 kg
The free-body diagram for the system is shown below: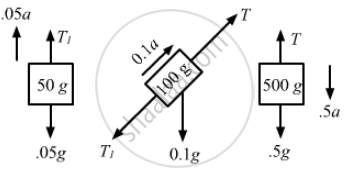
From the free-body diagram of the 500 g block,
T + 0.5a − 0.5g = 0 .....(i)
From the free-body diagram of the 50 g block,
T1 + 0.05g − 0.05a = a ....(ii)
From the free-body diagram of the 100 g block,
T1 + 0.1a − T + 0.5g = 0 ....(iii)
From equation (ii),
T1 = 0.05g + 0.05a .....(iv)
From equation (i),
T1 = 0.5g − 0.5a .....(v)
Equation (iii) becomes
T1 + 0.1a − T + 0.05g = 0
From equations (iv) and (v), we get:
0.05g + 0.05a + 0.1a − 0.5g + 0.5a + 0.05g = 0
0.65a = 0.4 g
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{0 . 4}{0 . 65}g\]
\[ = \frac{40}{65}g = \frac{8}{13}g \left(\text{ downward }\right)\]
So, the acceleration of the 500 gm block is
\[\frac{8g}{13}\] downward.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
A free 238U nucleus kept in a train emits an alpha particle. When the train is stationary, a nucleus decays and a passenger measures that the separation between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus becomes x at time t after the decay. If the decay takes place while the train is moving at a uniform velocity v, the distance between the alpha particle and the recoiling nucleus at a time t after the decay, as measured by the passenger, is
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
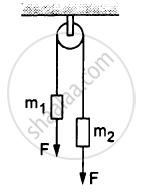
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
State the magnitude and direction of the force of gravity acting on the body of mass 5 kg. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
ame the law of motion which gives the definition of force.
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
