Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
उत्तर
Mass of the monkey, m = 15 kg,
Acceleration of the monkey in the upward direction, a = 1 m/s2
The free-body diagram of the monkey is shown below: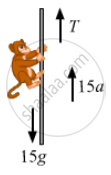
From the free-body diagram,
T − [15g + 15(a)] = 0
T − [15g + 15(1)] = 0
⇒ T = 5 (10 + 1)
⇒ T = 15 × 11 = 165 N
The monkey should apply a force of 165 N to the rope.
Initial velocity, u = 0
s = 5 m
Using, \[s = ut + \frac{1}{2}a t^2\], we get:
\[5 = 0 + \left( \frac{1}{2} \right) \times 1 \times t^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow t^2 = 5 \times 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt{10} s\]
Hence, the time required to reach the ceiling is \[\sqrt{10} s\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
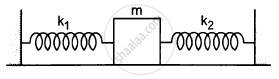
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm. Initially, the block B is near the right end of block A (In the following Figure). A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A. All the surfaces are assumed frictionless. Find the time that elapses before block B separates from A.

Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
The force of buoyancy exerted by the atmosphere on a balloon is B in the upward direction and remains constant. The force of air resistance on the balloon acts opposite the direction of velocity and is proportional to it. The balloon carries a mass M and is found to fall to the earth's surface with a constant velocity v. How much mass should be removed from the balloon so that it may rise with a constant velocity v?
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

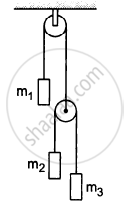
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
ame the law of motion which gives the definition of force.
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is ______.
