Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
Solution
Mass of the monkey, m = 15 kg,
Acceleration of the monkey in the upward direction, a = 1 m/s2
The free-body diagram of the monkey is shown below: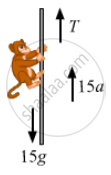
From the free-body diagram,
T − [15g + 15(a)] = 0
T − [15g + 15(1)] = 0
⇒ T = 5 (10 + 1)
⇒ T = 15 × 11 = 165 N
The monkey should apply a force of 165 N to the rope.
Initial velocity, u = 0
s = 5 m
Using, \[s = ut + \frac{1}{2}a t^2\], we get:
\[5 = 0 + \left( \frac{1}{2} \right) \times 1 \times t^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow t^2 = 5 \times 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt{10} s\]
Hence, the time required to reach the ceiling is \[\sqrt{10} s\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
Two blocks A and B of mass mA and mB , respectively, are kept in contact on a frictionless table. The experimenter pushes block A from behind, so that the blocks accelerate. If block A exerts force F on block B, what is the force exerted by the experimenter on block A?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
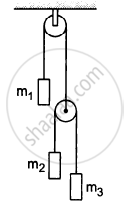
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
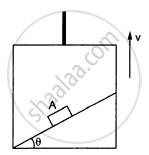
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
What will be its speed when it strikes the ground?
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
