Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
Solution
Mathematical expression of Newton's second law of motion is as shown below:
Force = Mass × Acceleration
Above relation holds for the following conditions:
(i) When the velocity of the body is much smaller than the velocity of light.
(ii) When the mass remains constant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.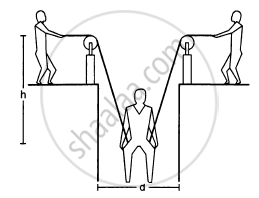
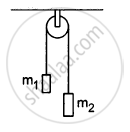
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

