Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

Solution
Given, the mass of the body (m) = 2 kg
From the position-time graph, the body is at x = 0 when t = 0, i.e., body is at rest.
∴ Impulse at t = 0, s = 0, is zero
From t =0 s to t = 4 s, the position-time graph is a straight line, which shows that body moves with uniform velocity.
Beyond t = 4 s, the graph is a straight line parallel to time ads, i.e., the body is at rest (v = 0).
The velocity of the body = slope of a position-time graph
= tan θ = `3/4` m/s
impulse (at t = 4 s) = change in momentum
= mv – mu
= m(v – u)
= `2(0 - 3/4)`
= `- 3/2` kg-m/s = – 1.5 kg-m/s
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
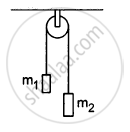
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
Which of the following are vector quantities?
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

