Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
Solution 1
(a) Mass of the helicopter, mh = 1000 kg
Mass of the crew and passengers, mp = 300 kg
Total mass of the system, m = 1300 kg
Acceleration of the helicopter, a = 15 m/s2
Using Newton’s second law of motion, the reaction force R, on the system by the floor can be calculated as:
R – mpg = ma
= mp(g + a)
= 300 (10 + 15) = 300 × 25
= 7500 N
Since the helicopter is accelerating vertically upward, the reaction force will also be directed upward. Therefore, as per Newton’s third law of motion, the force on the floor by the crew and passengers is 7500 N, directed downward.
(b) Using Newton’s second law of motion, the reaction force R’, experienced by the helicopter can be calculated as:
R' - mg = ma
=m(g+a)
=1300(10+15) = 1300 xx 25
= 32500 N
The reaction force experienced by the helicopter from the surrounding air is acting upward. Hence, as per Newton’s third law of motion, the action of the rotor on the surrounding air will be 32500 N, directed downward.
(c) The force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air is 32500 N, directed upward.
Solution 2
Here, mass of helicopter, m1= 1000 kg
Mass of the crew and passengers, m2 = 300 kg upward acceleration, a = 15 ms-2and g = 10 ms-2
(a)Force on the floor of helicopter by the crew and passengers = apparent weight of crew and passengers
= m2 (g + a) = 300 (10 + 15) N = 7500 N
(b)Action of rotor of helicopter on surrounding air is obviously vertically downwards, because helicopter rises on account of reaction to this force. Thus, force of action
F = (m1+ m2) (g + a) = (1000 + 300) (10 + 15) = 1300 x 25 = 32500 N
(c)Force on the helicopter due to surrounding air is the reaction. As action and reaction are equal and opposite, therefore, force of reaction, F = 32500 N, vertically upwards.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
Two blocks A and B of mass mA and mB , respectively, are kept in contact on a frictionless table. The experimenter pushes block A from behind, so that the blocks accelerate. If block A exerts force F on block B, what is the force exerted by the experimenter on block A?
The force of buoyancy exerted by the atmosphere on a balloon is B in the upward direction and remains constant. The force of air resistance on the balloon acts opposite the direction of velocity and is proportional to it. The balloon carries a mass M and is found to fall to the earth's surface with a constant velocity v. How much mass should be removed from the balloon so that it may rise with a constant velocity v?
Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

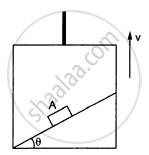
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
The motion of a particle of mass m is given by x = 0 for t < 0 s, x(t) = A sin 4 pt for 0 < t < (1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t > (1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true?
- The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is – 16π2 Am.
- The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s.
- The particle is not acted upon by any force.
- The particle is not acted upon by a constant force.
- There is no impulse acting on the particle.
