Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical circle of radius R. The net forces at the lowest and highest points of the circle directed vertically downwards are: [Choose the correct alternative]
| Lowest Point | Highest Point | |
| a) | mg – T1 | mg + T2 |
| b) | mg + T1 | mg – T2 |
| c) | `mg + T1 –(m_v_1^2)/R` | mg – T2 + (`mv_1^2`)/R |
| d) | `mg – T1 – (mv)/R` | mg + T2 + (mv_1^2)/R |
T1 and v1 denote the tension and speed at the lowest point. T2 and v2 denote corresponding values at the highest point.
Solution 1
(a)The free body diagram of the stone at the lowest point is shown in the following figure.
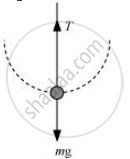
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the net force acting on the stone at this point is equal to the centripetal force, i.e.,
`F_"net" = T - mg = (mv_1^2)/R ...(i)`
Where, v1 = Velocity at the lowest point
The free body diagram of the stone at the highest point is shown in the following figure
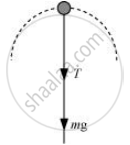
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we have:
`T + mg = (mv_2^2)/R `...(ii)
Where, v2 = Velocity at the highest point
It is clear from equations (i) and (ii) that the net force acting at the lowest and the highest points are respectively (T – mg) and (T + mg).
Solution 2
The net force at the lowest point is (mg – T1) and the net force at the highest point is (mg + T2). Therefore, alternative (a) is correct. Since mg and T1 are in mutually opposite directions at lowest point and mg and T2are in same direction at the highest point.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

The unit of linear momentum is :
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A ball is thrown upward and reaches a maximum height of 19.6 m. Find its initial speed?
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
Why does a child feel more pain when she falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

