Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does a child feel more pain when she falls down on a hard cement floor, than when she falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
Solution
The body of the child is brought to a sudden halt when she/he falls on a cement floor. The mud floor yields and the body travels some distance before it comes to rest, which takes some time. This means the force which brings the child to rest is less for the fall on a mud floor, as the change in momentum is brought about over a longer period.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
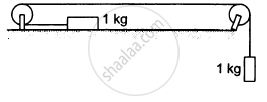
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
Which of the following are vector quantities?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
