Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
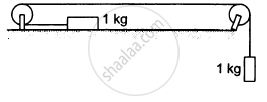
Solution
The free-body diagrams for both the bodies are shown below: 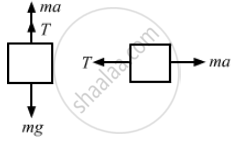
T + ma =mg ...(i)
and T = ma ...(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii), we get:
ma + ma = mg
⇒ 2ma = g
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{g}{2} = \frac{10}{5} = 5 m/ s^2\]
From equation (ii),
T = ma = 5 N
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
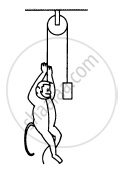
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
A small block B is placed on another block A of mass 5 kg and length 20 cm. Initially, the block B is near the right end of block A (In the following Figure). A constant horizontal force of 10 N is applied to the block A. All the surfaces are assumed frictionless. Find the time that elapses before block B separates from A.

A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.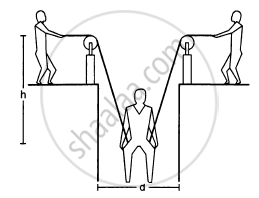
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

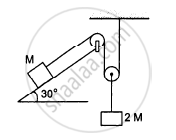
Find the acceleration of the block of mass M in the situation shown in the following figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and the pulleys and the string are light.
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
State two factors which determine the momentum of a body.
Name the physical entity used for quantifying the motion of a body.
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
