Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
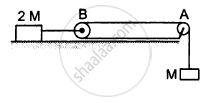
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
Solution
Let the acceleration of mass M be a.
So, the acceleration of mass 2M will be \[\frac{a}{2}\]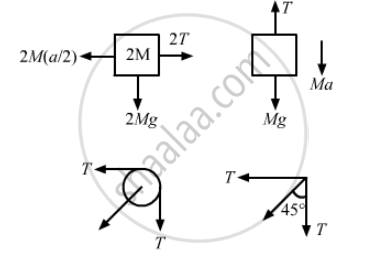
(a) 2M(a/2) − 2T = 0
⇒ Ma = 2T
T + Ma − Mg = 0
\[\Rightarrow \frac{Ma}{2} + Ma = Mg \]
\[ \Rightarrow 3Ma = 2Mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \frac{2g}{3}\]
(b) Tension,
\[T = \frac{Ma}{2} = \frac{M}{2} \times \frac{2g}{3} = \frac{Mg}{3}\]
(c) Let T' = resultant of tensions
\[\therefore T' = \sqrt{T^2 + T^2} = \sqrt{2}T\]
\[ \therefore T' = \sqrt{2}T = \frac{\sqrt{2}Mg}{3}\]
\[\text{Again, }\tan\theta = \frac{T}{T} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = 45^\circ\]
So, the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley is `(sqrt2"Mg")/3` at an angle of 45° with the horizontal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
Two blocks A and B of mass mA and mB , respectively, are kept in contact on a frictionless table. The experimenter pushes block A from behind, so that the blocks accelerate. If block A exerts force F on block B, what is the force exerted by the experimenter on block A?
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A stone is dropped freely from the top of a tower and it reaches the ground in 4 s. Taking g = 10m s-2, calculate the height of the tower.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
A body of mass 200 g is moving with a velocity of 5 ms−1. If the velocity of the body changes to 17 ms−1, calculate the change in linear momentum of the body.
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
