Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
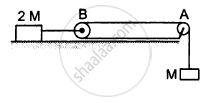
उत्तर
Let the acceleration of mass M be a.
So, the acceleration of mass 2M will be \[\frac{a}{2}\]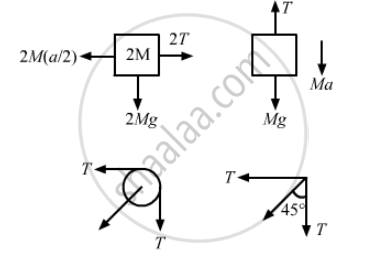
(a) 2M(a/2) − 2T = 0
⇒ Ma = 2T
T + Ma − Mg = 0
\[\Rightarrow \frac{Ma}{2} + Ma = Mg \]
\[ \Rightarrow 3Ma = 2Mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \frac{2g}{3}\]
(b) Tension,
\[T = \frac{Ma}{2} = \frac{M}{2} \times \frac{2g}{3} = \frac{Mg}{3}\]
(c) Let T' = resultant of tensions
\[\therefore T' = \sqrt{T^2 + T^2} = \sqrt{2}T\]
\[ \therefore T' = \sqrt{2}T = \frac{\sqrt{2}Mg}{3}\]
\[\text{Again, }\tan\theta = \frac{T}{T} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = 45^\circ\]
So, the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley is `(sqrt2"Mg")/3` at an angle of 45° with the horizontal.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving
- upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s-1
- downwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2
- upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2. What would be the readings on the scale in each case?
- What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity?
Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 15°. What is the radius of the loop?
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
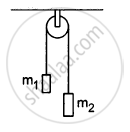
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
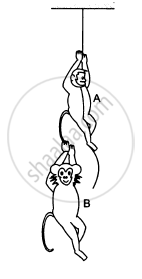
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
A ball is thrown upward and reaches a maximum height of 19.6 m. Find its initial speed?
A cricket ball of mass 150 g has an initial velocity `u = (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 and a final velocity `v = - (3hati + 4hatj)` m s−1 after being hit. The change in momentum (final momentum-initial momentum) is (in kg m s1)
