Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
उत्तर
We are pushed forward because of the inertia of motion, as our body opposes the sudden change.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
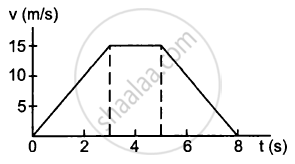
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
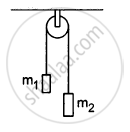
In a simple Atwood machine, two unequal masses m1 and m2 are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley. In a typical arrangement (In the following figure), m1 = 300 g and m2 = 600 g. The system is released from rest. (a) Find the distance travelled by the first block in the first two seconds; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) find the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley.
A tennis ball and a cricket ball , both are stationary. To start motion in them .
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
Prove mathematically F = ma
ame the law of motion which gives the definition of force.
What causes motion in a body?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
