Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
उत्तर
Mass of the body, m = 5kg
Velocity, v = 2 m/s
Linear momentum = mv = (5)(2) kg m/s
= 10 kg m/s-1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
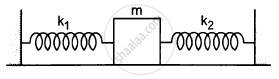
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
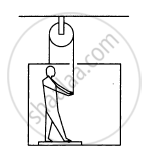
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
A ball is thrown vertically downward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. What is its speed 1 s later and 2 s later?
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

