Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
Solution
Mass of the body, m = 5kg
Velocity, v = 2 m/s
Linear momentum = mv = (5)(2) kg m/s
= 10 kg m/s-1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 15°. What is the radius of the loop?
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
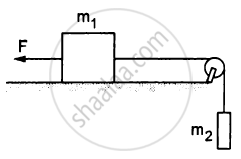
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

