Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
उत्तर
(i) Given, mass of the man = 60 kg
Let W' = apparent weight of the man in this case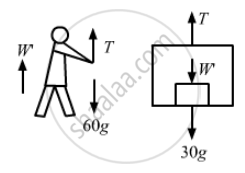
From the free-body diagram of the man,
W' + T − 60g = 0
⇒ T = 60g − W' ...(i)
From the free-body diagram of the box,
T − W' = 30g = 0 ...(ii)
From equation (i), we get:
60g − W' − W' − 30g = 0
⇒ W' = 15g
Hence, the weight recorded on the machine is 15 kg.
(ii) To find his actual weight, suppose the force applied by the men on the rope is T because of which the box accelerates upward with an acceleration a'.Here we need to find\[\ T'\]
Correct weight = W = 60g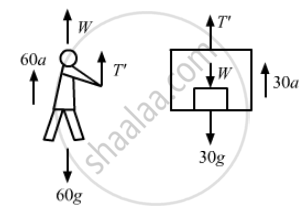
From the free-body diagram of the man,
T' + W − 60g − 60a = 0
⇒ T' − 60a = 0
⇒ T' = 60a ...(i)
From the free-body diagram of the box,
T' − W − 30g − 30a = 0
⇒ T' − 60g − 30g − 30a = 0
⇒ T' = 30a − 900 ...(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii), we get:
T' = 2T' − 1800
T' = 1800 N
So, the man should exert a force of 1800 N on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving
- upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s-1
- downwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2
- upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2. What would be the readings on the scale in each case?
- What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity?
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Prove mathematically F = ma
What causes motion in a body?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is ______.
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

