Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
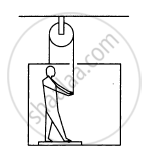
उत्तर
(i) Given, mass of the man = 60 kg
Let W' = apparent weight of the man in this case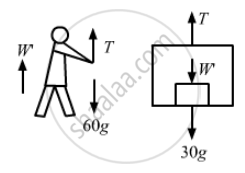
From the free-body diagram of the man,
W' + T − 60g = 0
⇒ T = 60g − W' ...(i)
From the free-body diagram of the box,
T − W' = 30g = 0 ...(ii)
From equation (i), we get:
60g − W' − W' − 30g = 0
⇒ W' = 15g
Hence, the weight recorded on the machine is 15 kg.
(ii) To find his actual weight, suppose the force applied by the men on the rope is T because of which the box accelerates upward with an acceleration a'.Here we need to find\[\ T'\]
Correct weight = W = 60g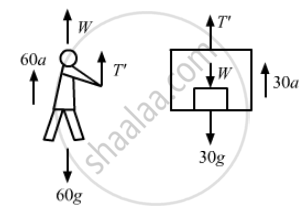
From the free-body diagram of the man,
T' + W − 60g − 60a = 0
⇒ T' − 60a = 0
⇒ T' = 60a ...(i)
From the free-body diagram of the box,
T' − W − 30g − 30a = 0
⇒ T' − 60g − 30g − 30a = 0
⇒ T' = 30a − 900 ...(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii), we get:
T' = 2T' − 1800
T' = 1800 N
So, the man should exert a force of 1800 N on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

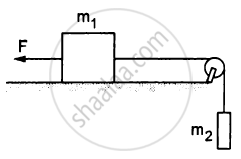
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
Which of the following are vector quantities?
What causes motion in a body?
Which of the following has the largest inertia?
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
