Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
उत्तर
The force of friction acting between my feet and ground is responsible for my deceleration.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
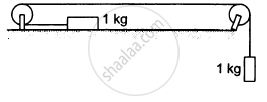
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
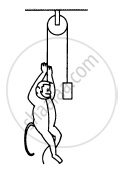
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
The motion of a particle of mass m is given by x = 0 for t < 0 s, x(t) = A sin 4 pt for 0 < t < (1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t > (1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true?
- The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is – 16π2 Am.
- The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s.
- The particle is not acted upon by any force.
- The particle is not acted upon by a constant force.
- There is no impulse acting on the particle.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

