Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
उत्तर
When the ceiling of the elevator is going up with an acceleration 'a', then a pseudo-force acts on the block in the downward direction.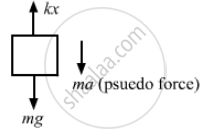
a = 2 m/s2
From the free-body diagram of the block,
kx = mg + ma
⇒ kx = 2g + 2a
= 2 × 9.8 + 2 × 2
= 19.6 + 4
\[\Rightarrow x = \frac{23 . 6}{100} = 0 . 236 \approx 0 . 24 \text{ m }\]
When 1 kg body is added,
total mass = (2 + 1) kg = 3 kg
Let elongation be x'.
∴ kx' = 3g + 3a = 3 × 9.8 + 6
\[ = 0 . 354 \approx 0 . 36 m\]
So, further elongation = x' − x
= 0.36 − 0.24 = 0.12 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
A block of mass 0.2 kg is suspended from the ceiling by a light string. A second block of mass 0.3 kg is suspended from the first block by another string. Find the tensions in the two strings. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
A tennis ball and a cricket ball , both are stationary. To start motion in them .
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
The unit of linear momentum is :
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
Prove mathematically F = ma
Name the physical entity used for quantifying the motion of a body.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
How long will it take to fall to the foot of the cliff?
A ball is thrown vertically downward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. What is its speed 1 s later and 2 s later?
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

