Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The force of buoyancy exerted by the atmosphere on a balloon is B in the upward direction and remains constant. The force of air resistance on the balloon acts opposite the direction of velocity and is proportional to it. The balloon carries a mass M and is found to fall to the earth's surface with a constant velocity v. How much mass should be removed from the balloon so that it may rise with a constant velocity v?
उत्तर
Let M be mass of the balloon.
Let the air resistance force on balloon be F .
Given that F ∝ v.
⇒ F = kv,
where k = proportionality constant.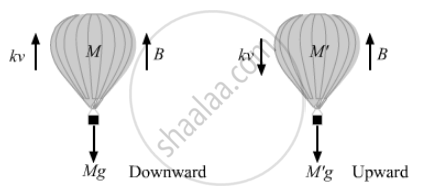
When the balloon is moving downward with constant velocity,
B + kv = Mg ...(i)
\[\Rightarrow M = \frac{B + kv}{g}\]
Let the mass of the balloon be M' so that it can rise with a constant velocity v in the upward direction.
B = Mg + kv
\[\Rightarrow M' = \frac{B + kv}{g}\]
∴ Amount of mass that should be removed = M − M'.
\[∆ M = \frac{B + kv}{g} - \frac{B - kv}{g}\]
\[ = \frac{B + kv - B + kv}{g}\]
\[ = \frac{2kv}{g} = \frac{2\left( Mg - B \right)}{g}\]
\[ = 2\left\{ M - \frac{B}{g} \right\}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
Two blocks A and B of mass mA and mB , respectively, are kept in contact on a frictionless table. The experimenter pushes block A from behind, so that the blocks accelerate. If block A exerts force F on block B, what is the force exerted by the experimenter on block A?
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.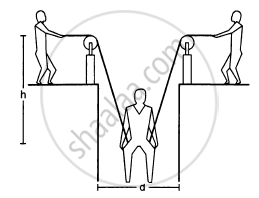
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
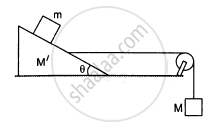
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
State the magnitude and direction of the force of gravity acting on the body of mass 5 kg. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
Calculate the velocity of a body of mass 0.5 kg, when it has a linear momentum of 5 Ns.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
ame the law of motion which gives the definition of force.
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
Which of the following has the largest inertia?
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
