Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
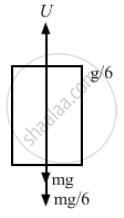
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
उत्तर
Let U be the upward force of water acting on the plastic box.
Let m be the initial mass of the plastic box.
When the empty plastic box is accelerating upward,
\[U - mg = \frac{mg}{6}\]
\[ \Rightarrow U = \frac{7 mg}{6}\]
\[\Rightarrow m = \frac{6U}{7g} . . . . \left( i \right)\]
Let M be the final mass of the box after putting some sand in it.
\[Mg - U = \frac{Mg}{6}\]
\[ \Rightarrow Mg - \frac{Mg}{6} = U\]
\[ \Rightarrow M = \frac{6U}{5g} . . . . \left( ii \right)\]
Mass added
\[= \frac{6U}{5g} - \frac{6U}{7g}\]
\[= \frac{6U\left( 7 - 5 \right)}{35 g}\]
\[ = \frac{6U \cdot 2}{35 g}\]
From equation (i),
\[m = \frac{6U}{7g}\]
∴ Mass added
\[= \frac{2}{5}m\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

The rear side of a truck is open and a box of 40 kg mass is placed 5 m away from the open end as shown in Figure. The coefficient of friction between the box and the surface below it is 0.15. On a straight road, the truck starts from rest and accelerates with 2 m s–2. At what distance from the starting point does the box fall off the truck? (Ignore the size of the box).

If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.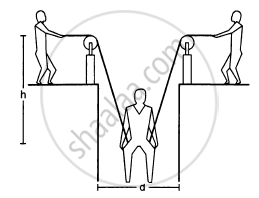
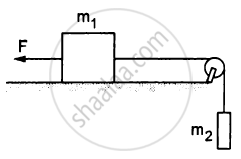
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
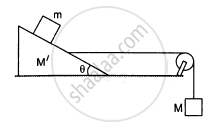
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
Define linear momentum and state its S.I. unit.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
State Newton's second law of motion. Is Newton's first law of motion contained in Newton's second law of motion?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
The motion of a particle of mass m is given by x = 0 for t < 0 s, x(t) = A sin 4 pt for 0 < t < (1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t > (1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true?
- The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is – 16π2 Am.
- The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s.
- The particle is not acted upon by any force.
- The particle is not acted upon by a constant force.
- There is no impulse acting on the particle.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

