Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.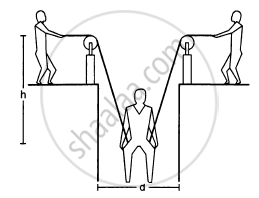
उत्तर
(a) At any depth, let the ropes makes an angle θ with the vertical.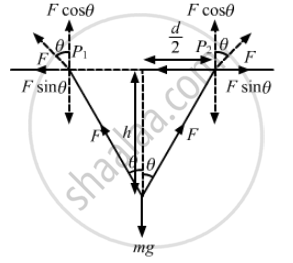
From the free-body diagram,
Fcosθ + Fcosθ − mg = 0
2Fcosθ = mg
\[\Rightarrow F = \frac{mg}{2cos\theta}\]
As the man moves up, θ increases, i.e. cosθ decreases. Thus, F increases.
\[\cos\theta = \frac{h}{\sqrt{\left( d/2 \right)^2 + h^2}}\]
(b) When the man is at depth h,
\[F = \frac{mg}{2\cos\theta}\]
\[ = \frac{mg}{2\left[ h/\sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + h^2} \right]}\]
\[ = \frac{mg}{4h}\sqrt{d^2 + 4 h^2}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms–1. How long does the body take to stop?
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
In a TV picture tube, electrons are ejected from the cathode with negligible speed and they attain a velocity of 5 × 106 m/s in travelling one centimetre. Assuming straight-line motion, find the constant force exerted on the electrons. The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 kg.
A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The elevator starts going up with some acceleration, moves with uniform velocity for a while and finally decelerates to stop. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 72 kg and 60 kg, respectively. Assuming that the magnitudes of acceleration and deceleration are the same, find (a) the true weight of the person and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration. Take g = 9.9 m/s2.
Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with velocity 2 m s-1. Calculate its linear momentum.
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
How long will a stone take to fall to the ground from the top of a building 80 m high
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
The motion of a particle of mass m is given by x = 0 for t < 0 s, x(t) = A sin 4 pt for 0 < t < (1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t > (1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true?
- The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is – 16π2 Am.
- The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s.
- The particle is not acted upon by any force.
- The particle is not acted upon by a constant force.
- There is no impulse acting on the particle.
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
