Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

उत्तर
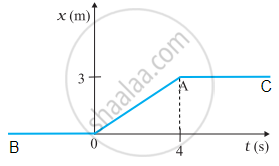
- For t < 0
For t<0, the graph of position versus time is denoted as BO, which indicates that the displacement of the particle is zero, i.e., the particle is stationary at the origin. Consequently, the force exerted on the particle must be zero. - For t > 4 s
For t>4 s, the position-time graph segment AC runs parallel to the time axis, indicating that the particle maintains a position 3 metres from the origin, implying it is stationary. Therefore, the force acting on the particle is zero. - For 0 < t < 4
Between 0 < t < 4 s, the position-time graph labelled OA displays a constant slope, which indicates that the velocity of the particle remains constant during this interval, meaning the particle has zero acceleration. Consequently, the force on the particle must be zero.
- For t < 0
- At t = 0
Impulse = Change in momentum
= mv – mu
Mass of the particle, m = 4 kg
Initial velocity of the particle, u = 0
Final velocity of the particle, `v = 3/4 "m/s"`
∴Impulse = `4(3/4 - 0) = 3 kg "m/s"`
At t = 4 s
Initial velocity of the particle, `u = 3/4 "m/s"`
Final velocity of the particle, v = 0
∴ Impulse = `4(0-3/4)` = -3 kg m/s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.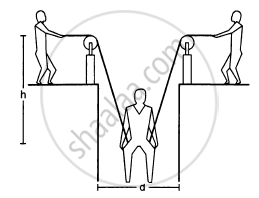
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
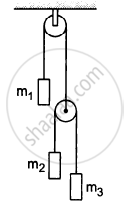
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
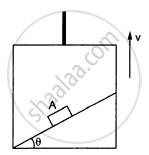
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate : The magnitude of the force
A bullet of mass 50 g moving with an initial velocity 100 m s-1 strikes a wooden block and comes to rest after penetrating a distance 2 cm in it. Calculate: (i) Initial momentum of the bullet, (ii) Final momentum of the bullet, (iii) Retardation caused by the wooden block and (iv) Resistive force exerted by the wooden block.
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
