Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
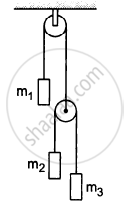
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
उत्तर
The free-body diagram for mass m1 is shown below: a
a
The free-body diagram for mass m2 is shown below: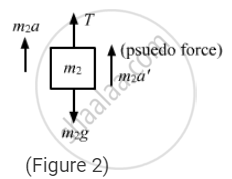
The free-body diagram for mass m3 is shown below: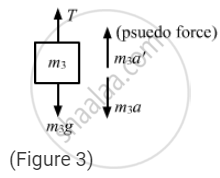
Suppose the block m1 moves upward with acceleration a1 and the blocks m2 and m3have relative acceleration a2 due to the difference of weight between them.
So, the actual acceleration of the blocks m1, m2 and m3 will be a1, (a1 − a2) and (a1 + a2), as shown.
From figure 2, T − 1g − 1a1 = 0 ...(i)
From figure 3,\[\frac{T}{2} - 2g - 2\left( a_1 - a_2 \right) = 0 . . . \left( ii \right)\]
From figure 4,\[\frac{T}{2} - 3g - 3\left( a_1 + a_2 \right) = 0 . . . \left( iii \right)\]
From equations (i) and (ii), eliminating T, we get:
1g + 1a2 = 4g + 4 (a1 + a2)
5a2 − 4a1 = 3g ...(iv)
From equations (ii) and (iii), we get:
2g + 2(a1 − a2) = 3g − 3 (a1 − a2)
5a1 + a2 = g ...(v)
Solving equations (iv) and (v), we get:
\[a_1 = \frac{2g}{29}\]
\[\text{ and }a_2 = g - 5 a_1 \]
\[ \Rightarrow a_2 = g - \frac{10g}{29} = \frac{19g}{29}\]
\[\text{So}, a_1 - a_2 = \frac{2g}{29} - \frac{19g}{29} = - \frac{17g}{29}\]
So, accelerations of m1, m2 and m3 are \[\frac{19g}{29}\left( up \right),
\frac{17g}{29} \left(\text{ down }\right)\text{ and }\frac{21g}{29}\left(\text{ down }\right)\]
Now, u = 0, s = 20 cm = 0.2 m
\[a_2 = \frac{19g}{29} \]
\[ \therefore s = ut + \frac{1}{2}a t^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow 0 . 2 = \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{19}{29}g t^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow t = 0 . 25 s\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
A person drops a coin. Describe the path of the coin as seen by the person if he is in (a) a car moving at constant velocity and (b) in a free falling elevator.
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

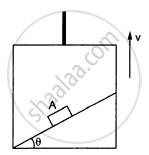
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
The position time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in figure. What is the impulse on the body at t = 0 s and t = 4 s.

