Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A person drops a coin. Describe the path of the coin as seen by the person if he is in (a) a car moving at constant velocity and (b) in a free falling elevator.
उत्तर
When the person drops the coin, the path of coin as seen by the person if:
a) In the car, the path of the coin will be vertically downward because the only force acting on the coin is gravity in the downward direction.
(b) In a free falling elevator, the coin as well as the person will be in a condition of weightlessness. So, the coin will remain stationary with respect to the person.
Because all fee falls objects weightlessness.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical circle of radius R. The net forces at the lowest and highest points of the circle directed vertically downwards are: [Choose the correct alternative]
| Lowest Point | Highest Point | |
| a) | mg – T1 | mg + T2 |
| b) | mg + T1 | mg – T2 |
| c) | `mg + T1 –(m_v_1^2)/R` | mg – T2 + (`mv_1^2`)/R |
| d) | `mg – T1 – (mv)/R` | mg + T2 + (mv_1^2)/R |
T1 and v1 denote the tension and speed at the lowest point. T2 and v2 denote corresponding values at the highest point.
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
The rear side of a truck is open and a box of 40 kg mass is placed 5 m away from the open end as shown in Figure. The coefficient of friction between the box and the surface below it is 0.15. On a straight road, the truck starts from rest and accelerates with 2 m s–2. At what distance from the starting point does the box fall off the truck? (Ignore the size of the box).

A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
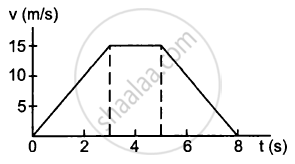
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

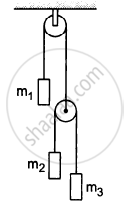
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
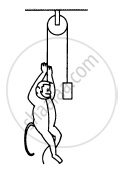
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
A ball is thrown upward and reaches a maximum height of 19.6 m. Find its initial speed?
