Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
पर्याय
mg
mg/cosθ
mg cosθ
mg tanθ
उत्तर
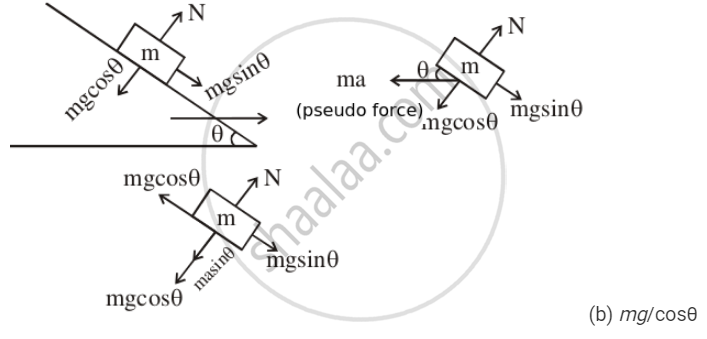
Free-body Diagram of the Small Block of Mass 'm'
The block is at equilibrium w.r.t. to wedge. Therefore,
mg sinθ = ma cosθ
⇒ a = gtanθ
Normal reaction on the block is
N = mg cosθ + ma sinθ
Putting the value of a, we get:
N = mg cosθ + mg tanθsinθ
\[N = mg\cos\theta + mg\frac{\sin\theta}{\cos\theta}\sin\ \theta N=\frac{mg}{\cos\theta}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a TV picture tube, electrons are ejected from the cathode with negligible speed and they attain a velocity of 5 × 106 m/s in travelling one centimetre. Assuming straight-line motion, find the constant force exerted on the electrons. The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 kg.
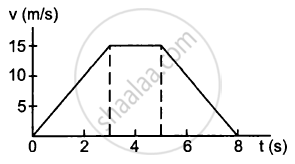
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
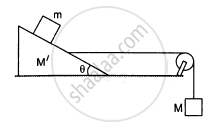
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
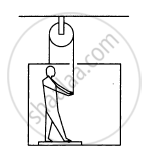
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
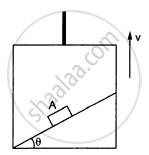
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
How can Newton's first law of motion be obtained from the second law of motion?
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
What causes motion in a body?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
