Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
उत्तर

For m1 to be at rest, a1 = 0.
T − m1g = 0
T = m1g ...(i)
For mass m2,
T/2 − 2g = 2a
T = 4a + 4g ...(ii)
For mass m3,
3g – T/2= 2a
T = 6g − 6a ...(ii)
From equations (ii) and (iii), we get:
3T – 12g = 12g – 2T
T = 24g/5= 4.08g
Putting the value of T in equation (i), we get:
m1 = 4.8kg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
In a TV picture tube, electrons are ejected from the cathode with negligible speed and they attain a velocity of 5 × 106 m/s in travelling one centimetre. Assuming straight-line motion, find the constant force exerted on the electrons. The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10−31 kg.
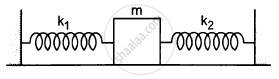
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

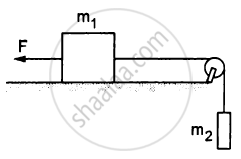
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
Calculate the velocity of a body of mass 0.5 kg, when it has a linear momentum of 5 Ns.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Prove mathematically F = ma
What causes motion in a body?
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
We always prefer to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump.
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is ______.
