Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is ______.
पर्याय
136 N
134 N
158 N
68 N
उत्तर
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is 136 N.
Explanation:
Given, mass = 2 kg
`x(t) = pt + qt^2 + rt^3`
`v = (dx)/(dt) = p + 2qt + 3rt^2`
`a = (dv)/(dt) = 0 + 2q + 6rt`
At t = 2s; a = 2q + 6 × 2 × r
= 2q + 12r
= 2 × 4 + 12 × 5
= 8 + 60
= 68 m/s
Force = F = ma
= 2 × 68
= 136 N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
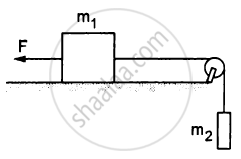
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
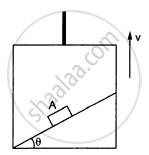
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
Name the physical entity used for quantifying the motion of a body.
