Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
उत्तर
Horizontal force, F = 600 N
Mass of body A, m1 = 10 kg
Mass of body B, m2 = 20 kg
Total mass of the system, m = m1 + m2 = 30 kg
Using Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration (a) produced in the system can be calculated as:
F = ma
`:.a = F/m = 600/30 = 20 "m/s"^2`
(i) When force F is applied to body A:
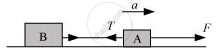
The equation of motion can be written as:
F-T = m1a
T = F - m1a
= 600 – 10 × 20 = 400 N
(ii) When force F is applied to body B:
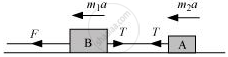
The equation of motion can be written as:
F – T = m2a
T = F – m2a
∴T = 600 – 20 × 20 = 200 N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical circle of radius R. The net forces at the lowest and highest points of the circle directed vertically downwards are: [Choose the correct alternative]
| Lowest Point | Highest Point | |
| a) | mg – T1 | mg + T2 |
| b) | mg + T1 | mg – T2 |
| c) | `mg + T1 –(m_v_1^2)/R` | mg – T2 + (`mv_1^2`)/R |
| d) | `mg – T1 – (mv)/R` | mg + T2 + (mv_1^2)/R |
T1 and v1 denote the tension and speed at the lowest point. T2 and v2 denote corresponding values at the highest point.
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
A man has fallen into a ditch of width d and two of his friends are slowly pulling him out using a light rope and two fixed pulleys as shown in the following figure. Show that the force (assumed equal for both the friends) exerted by each friend on the road increases as the man moves up. Find the force when the man is at a depth h.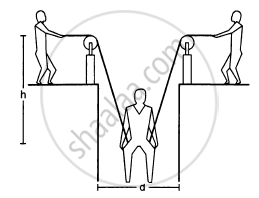
Find the acceleration of the blocks A and B in the three situations shown in the following figure.

A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
How long will it take to fall to the foot of the cliff?
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
A hockey player is moving northward and suddenly turns westward with the same speed to avoid an opponent. The force that acts on the player is ______.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

