Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical circle of radius R. The net forces at the lowest and highest points of the circle directed vertically downwards are: [Choose the correct alternative]
| Lowest Point | Highest Point | |
| a) | mg – T1 | mg + T2 |
| b) | mg + T1 | mg – T2 |
| c) | `mg + T1 –(m_v_1^2)/R` | mg – T2 + (`mv_1^2`)/R |
| d) | `mg – T1 – (mv)/R` | mg + T2 + (mv_1^2)/R |
T1 and v1 denote the tension and speed at the lowest point. T2 and v2 denote corresponding values at the highest point.
उत्तर १
(a)The free body diagram of the stone at the lowest point is shown in the following figure.
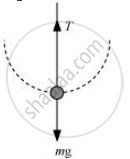
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the net force acting on the stone at this point is equal to the centripetal force, i.e.,
`F_"net" = T - mg = (mv_1^2)/R ...(i)`
Where, v1 = Velocity at the lowest point
The free body diagram of the stone at the highest point is shown in the following figure
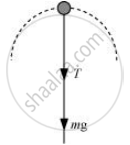
Using Newton’s second law of motion, we have:
`T + mg = (mv_2^2)/R `...(ii)
Where, v2 = Velocity at the highest point
It is clear from equations (i) and (ii) that the net force acting at the lowest and the highest points are respectively (T – mg) and (T + mg).
उत्तर २
The net force at the lowest point is (mg – T1) and the net force at the highest point is (mg + T2). Therefore, alternative (a) is correct. Since mg and T1 are in mutually opposite directions at lowest point and mg and T2are in same direction at the highest point.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
Suppose you are running fast in a field and suddenly find a snake in front of you. You stop quickly. Which force is responsible for your deceleration?
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The elevator starts going up with some acceleration, moves with uniform velocity for a while and finally decelerates to stop. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 72 kg and 60 kg, respectively. Assuming that the magnitudes of acceleration and deceleration are the same, find (a) the true weight of the person and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration. Take g = 9.9 m/s2.
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

A body of mass m moving with a velocity v is acted upon by a force. Write an expression for change in momentum in each of the following cases: (i) When v << c, (ii) When v → c and (iii) When v << c but m does not remain constant. Here, c is the speed of light.
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
State the magnitude and direction of the force of gravity acting on the body of mass 5 kg. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
