Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The elevator starts going up with some acceleration, moves with uniform velocity for a while and finally decelerates to stop. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 72 kg and 60 kg, respectively. Assuming that the magnitudes of acceleration and deceleration are the same, find (a) the true weight of the person and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration. Take g = 9.9 m/s2.
उत्तर

Maximum weight will be recorded when the elevator accelerates upwards.
Let N be the normal reaction on the person by the weighing machine.
So, from the free-body diagram of the person,
\[N = mg + ma\] ...(1)
This is maximum weight, N = 72 × 9.9 N
When decelerating upwards, minimum weight will be recorded.
\[N' = mg + m\left( - a \right)\] ...(2)
This is minimum weight, N' = 60 × 9.9 N
From equations (1) and (2), we have:
2 mg = 1306.8
\[\Rightarrow m = \frac{1306 . 8}{2 \times 9 . 9} = 66 kg\]
So, the true mass of the man is 66 kg.
And true weight = 66 \[\times\] 9.9 = 653.4 N
(b) Using equation (1) to find the acceleration, we get:
mg + ma = 72 × 9.9
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{72 \times 9 . 9 - 66 \times 9 . 9}{66} = \frac{9 . 9 \times 6}{66} = \frac{9 . 9}{11}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 0 . 9 m/ s^2\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
The below figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg.
- What is the force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
- What is the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one-dimensional motion only.)

Two masses 8 kg and 12 kg are connected at the two ends of a light, inextensible string that goes over a frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of the masses, and the tension in the string when the masses are released.
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
When a horse pulls a cart, the force that helps the horse to move forward is the force exerted by
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
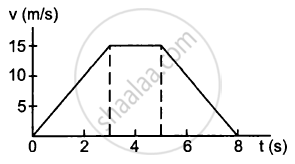
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
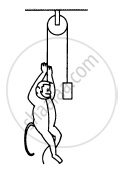
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
Which of the following are vector quantities?
Which of the following has the largest inertia?
Name the physical quantity which equals the rate of change of linear momentum.
What do you mean by an impulsive force?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
