Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The elevator starts going up with some acceleration, moves with uniform velocity for a while and finally decelerates to stop. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 72 kg and 60 kg, respectively. Assuming that the magnitudes of acceleration and deceleration are the same, find (a) the true weight of the person and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration. Take g = 9.9 m/s2.
उत्तर

Maximum weight will be recorded when the elevator accelerates upwards.
Let N be the normal reaction on the person by the weighing machine.
So, from the free-body diagram of the person,
\[N = mg + ma\] ...(1)
This is maximum weight, N = 72 × 9.9 N
When decelerating upwards, minimum weight will be recorded.
\[N' = mg + m\left( - a \right)\] ...(2)
This is minimum weight, N' = 60 × 9.9 N
From equations (1) and (2), we have:
2 mg = 1306.8
\[\Rightarrow m = \frac{1306 . 8}{2 \times 9 . 9} = 66 kg\]
So, the true mass of the man is 66 kg.
And true weight = 66 \[\times\] 9.9 = 653.4 N
(b) Using equation (1) to find the acceleration, we get:
mg + ma = 72 × 9.9
\[\Rightarrow a = \frac{72 \times 9 . 9 - 66 \times 9 . 9}{66} = \frac{9 . 9 \times 6}{66} = \frac{9 . 9}{11}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 0 . 9 m/ s^2\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical circle of radius R. The net forces at the lowest and highest points of the circle directed vertically downwards are: [Choose the correct alternative]
| Lowest Point | Highest Point | |
| a) | mg – T1 | mg + T2 |
| b) | mg + T1 | mg – T2 |
| c) | `mg + T1 –(m_v_1^2)/R` | mg – T2 + (`mv_1^2`)/R |
| d) | `mg – T1 – (mv)/R` | mg + T2 + (mv_1^2)/R |
T1 and v1 denote the tension and speed at the lowest point. T2 and v2 denote corresponding values at the highest point.
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the elevator may be
(a) going up with increasing speed
(b) going down with increasing speed
(c) going up with uniform speed
(d) going down with uniform speed
A person says that he measured the acceleration of a particle to be non-zero even though no force was acting on the particle.
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
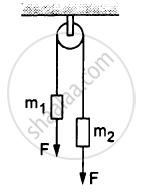
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
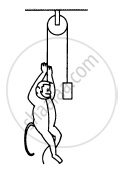
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
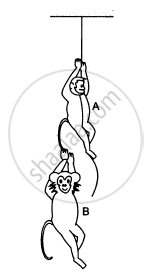
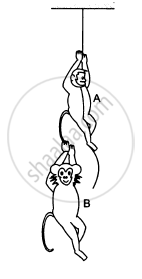
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
Two bodies A and B of same mass are moving with velocities v and 2v, respectively. Compare their (i) inertia and (ii) momentum.
Two balls A and B of masses m and 2 m are in motion with velocities 2v and v, respectively. Compare:
(i) Their inertia.
(ii) Their momentum.
(iii) The force needed to stop them in the same time.
State the Newton's second law of motion. What information do you get from it?
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
