Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

उत्तर
Let the left and right blocks be A and B, respectively.
And let the acceleration of the 3 kg mass relative to the elevator be 'a' in the downward direction.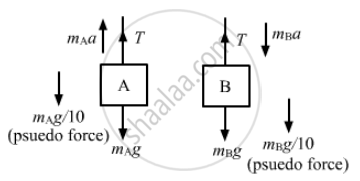
From the free-body diagram,
\[m_A a = T - m_A g - \frac{m_A g}{10} . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
\[m_B a = m_B g + \frac{m_B g}{10} - T . . . \left( 2 \right)\]
Adding both the equations, we get:
\[a\left( m_A + m_B \right) = \left( m_B - m_A \right)g + \left( m_B - m_A \right)\frac{g}{10}\]
Putting value of the masses,we get:
\[9a = \frac{33g}{10}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{a}{g} = \frac{11}{30} . . . \left( 3 \right)\]
Now, using equation (1), we get:
\[T = m_A \left( a + g + \frac{g}{10} \right)\]
The reading of the spring balance =\[\frac{2T}{g} = \frac{2}{g} m_A \left( a + g + \frac{g}{10} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2 \times 1 . 5\left( \frac{a}{g} + 1 + \frac{1}{10} \right) = 3\left( \frac{11}{30} + 1 + \frac{1}{10} \right)\]
= 4 . 4 kg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
You are travelling in a car. The driver suddenly applies the brakes and you are pushed forward. Why does this happen?
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
Write the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion. State the conditions if any.
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
The linear momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v is :
State the magnitude and direction of the force of gravity acting on the body of mass 5 kg. Take g = 9.8 m s-2.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A pebble is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 20 m s-1. How high will it be after 2 s? (Take g = 10 m s-2)
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
What do you mean by an impulsive force?
A ball is thrown vertically downward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. What is its speed 1 s later and 2 s later?
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

