Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

Solution
Let the left and right blocks be A and B, respectively.
And let the acceleration of the 3 kg mass relative to the elevator be 'a' in the downward direction.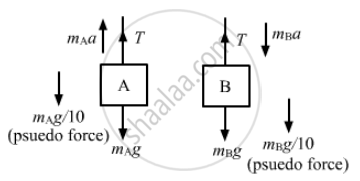
From the free-body diagram,
\[m_A a = T - m_A g - \frac{m_A g}{10} . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
\[m_B a = m_B g + \frac{m_B g}{10} - T . . . \left( 2 \right)\]
Adding both the equations, we get:
\[a\left( m_A + m_B \right) = \left( m_B - m_A \right)g + \left( m_B - m_A \right)\frac{g}{10}\]
Putting value of the masses,we get:
\[9a = \frac{33g}{10}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{a}{g} = \frac{11}{30} . . . \left( 3 \right)\]
Now, using equation (1), we get:
\[T = m_A \left( a + g + \frac{g}{10} \right)\]
The reading of the spring balance =\[\frac{2T}{g} = \frac{2}{g} m_A \left( a + g + \frac{g}{10} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2 \times 1 . 5\left( \frac{a}{g} + 1 + \frac{1}{10} \right) = 3\left( \frac{11}{30} + 1 + \frac{1}{10} \right)\]
= 4 . 4 kg
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
Two blocks A and B of mass mA and mB , respectively, are kept in contact on a frictionless table. The experimenter pushes block A from behind, so that the blocks accelerate. If block A exerts force F on block B, what is the force exerted by the experimenter on block A?
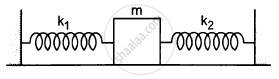
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
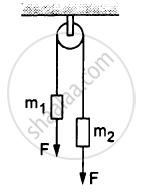
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
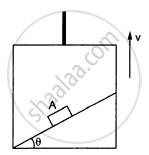
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
How can Newton's first law of motion be obtained from the second law of motion?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
Which of the following are vector quantities?
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body?
Use Newton's second law to explain the following:
While catching a fast moving ball, we always pull our hands backwards.
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
What will be its speed when it strikes the ground?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
What do you mean by the conservation of momentum? Briefly, explain the collision between two bodies and the conservation of momentum.
A woman throws an object of mass 500 g with a speed of 25 ms1.
- What is the impulse imparted to the object?
- If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
