Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
Solution
Given,
mass of the first block, m = 2 kg
k = 100 N/m
Let elongation in the spring be x. 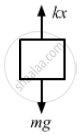
From the free-body diagram,
kx = mg
\[x = \frac{mg}{k} = \frac{2 \times 9 . 8}{100}\]
\[ = \frac{19 . 6}{100} = 0 . 196 \approx 0 . 2 m\]
Suppose, further elongation, when the 1 kg block is added, is \[∆ x\] Then, \[k\left( x + ∆ x \right) = m'g\]
⇒ k \[∆ x\] 3g − 2g = g
\[\Rightarrow ∆ x = \frac{g}{k} = \frac{9 . 8}{100} = 0 . 098 \approx 0 . 1 m\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When a carpet is beaten with a stick, dust comes out of it. Explain.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed.
If the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks?
What is the other name of Newton’s first law of motion ?
Define one newton force.
The acceleration of a particle is zero, as measured from an inertial frame of reference. Can we conclude that no force acts on the particle?
Consider a book lying on a table. The weight of the book and the normal force by the table in the book are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Is this an example of Newton's third law?
A particle stays at rest as seen in a frame. We can conclude that
(a) the frame is inertial
(b) resultant force on the particle is zero
(c) the frame may be inertial but the resultant force on the particle is zero
(d) the frame may be non-inertial but there is a non-zero resultant force
A particle is observed from two frames S1 and S2. Frame S2 moves with respect to S1with an acceleration a. Let F1 and F2 be the pseudo forces on the particle when seen from S1 and S2, respectively. Which of the following is not possible?
A block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant force F. It is found to move 10 m in the first seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
A force of 600 dynes acts on a glass ball of mass 200 g for 12 s. If initially, the ball is at rest, find
- Final velocity
- Distance covered.
Give one example each of inertia of rest and inertia of motion.
The greater is the __________ the greater is the inertia of an object.
Differentiate between gravitational mass and inertial mass.
In the above given problem if the lower thread is pulled with a jerk, what happens?
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
