Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
उत्तर
Given,
mass of the first block, m = 2 kg
k = 100 N/m
Let elongation in the spring be x. 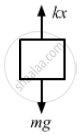
From the free-body diagram,
kx = mg
\[x = \frac{mg}{k} = \frac{2 \times 9 . 8}{100}\]
\[ = \frac{19 . 6}{100} = 0 . 196 \approx 0 . 2 m\]
Suppose, further elongation, when the 1 kg block is added, is \[∆ x\] Then, \[k\left( x + ∆ x \right) = m'g\]
⇒ k \[∆ x\] 3g − 2g = g
\[\Rightarrow ∆ x = \frac{g}{k} = \frac{9 . 8}{100} = 0 . 098 \approx 0 . 1 m\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The driver of a three-wheeler moving with a speed of 36 km/h sees a child standing in the middle of the road and brings his vehicle to rest in 4.0 s just in time to save the child. What is the average retarding force on the vehicle? The mass of the three-wheeler is 400 kg and the mass of the driver is 65 kg.
If the speed of the stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value, and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks?
What is the other name of Newton’s first law of motion ?
Name the scientist who gave the laws of motion.
Define one newton force.
It is sometimes heard that the inertial frame of reference is only an ideal concept and no such inertial frame actually exists. Comment.
Neglect the effect of rotation of the earth. Suppose the earth suddenly stops attracting objects placed near its surface. A person standing on the surface of the earth will.
In an imaginary atmosphere, the air exerts a small force F on any particle in the direction of the particle's motion. A particle of mass m projected upward takes time t1 in reaching the maximum height and t2 in the return journey to the original point. Then.
'When a hanging carpet is beaten with a stick, the dust particles start coming out of it'. This phenomenon can be best explained by making use of :
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
Derive the relation between newton and dyne.
What do you mean by inertia of motion?
Name the different kinds of inertia an object can possess. Give an example of each.
Define one Newton.
If a 5 N and a 15 N forces are acting opposite to one another. Find the resultant force and the direction of action of the resultant force.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

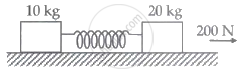
The masses of 10 kg and 20 kg, respectively, are connected by massless spring as shown in the figure. A force of 200 N acts on the 20 kg mass. At the instant shown, the 10 kg mass has acceleration of 12 m/s2. What is the acceleration of 20 kg mass?
(g = 10 m/s2)
A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

