Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The driver of a three-wheeler moving with a speed of 36 km/h sees a child standing in the middle of the road and brings his vehicle to rest in 4.0 s just in time to save the child. What is the average retarding force on the vehicle? The mass of the three-wheeler is 400 kg and the mass of the driver is 65 kg.
उत्तर
Initial speed of the three-wheeler, u = 36 km/h
= 36 × (5/18) m/s
= 10 m/s
Final speed of the three-wheeler, v = 0 m/s
Time, t = 4 s
Mass of the three-wheeler, m = 400 kg
Mass of the driver, m' = 65 kg
Total mass of the system, M = 400 + 65 = 465 kg
Using the first law of motion, the acceleration (a) of the three-wheeler can be calculated as:
v = u + at
`:. a =(v-u)/t = (0 - 10)/4 = -2.5 "m/s"^2`
The negative sign signifies that the velocity of the three-wheeler is reducing over time.
Using Newton’s second law of motion, the net force acting on the three-wheeler can be calculated as:
F = Ma
= 465 × (-2.5) = -1162.5 N = 1.2 × 103 N
The negative sign suggests that the force is applied in opposition to the direction of motion of the three-wheeler.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
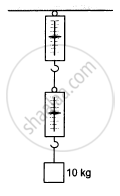
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
Neglect the effect of rotation of the earth. Suppose the earth suddenly stops attracting objects placed near its surface. A person standing on the surface of the earth will.
Three rigid rods are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. Three particles carrying charges 20 μC each are attached to the vertices of the triangle. The whole system is at rest in an inertial frame. The magnitude of the resultant force on the charged particle at A is.
A force of 600 dynes acts on a glass ball of mass 200 g for 12 s. If initially, the ball is at rest, find
- Final velocity
- Distance covered.
What do you mean by inertia of motion?
What do you mean by inertia of rest?
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (figure). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictonless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.

Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2 m, respectively, are held at rest such that the spring is in natural length. Find out the accelerations of both the blocks just after release.

A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
