Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (figure). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictonless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.

उत्तर
In equilibrium, the force mg sin θ acting on block A parallel to the plane should be balanced by the tension in the string, ie.,
mg sin θ = T = F [∵ T = F given] ......(i)
And for block B, w = T = F ......(ii)
Where w is the weight of block B.
From equations (i) and (ii), we get,
w = mg sin θ
= 100 × sin 30° .....[∵ mg = 100 N]
= `100 xx 1/2` N
= 50 N
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define one newton force.
Name the law involved in the following situation :
if there were no friction and no air resistance, then a moving bicycle would go on moving for ever.
It is sometimes heard that the inertial frame of reference is only an ideal concept and no such inertial frame actually exists. Comment.
A plumb bob is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. If the train moves with an acceleration 'a' along a straight horizontal track , the string supporting the bob makes an angle tan−1 (a/g) with the normal to the ceiling. Suppose the train moves on an inclined straight track with uniform velocity. If the angle of incline is tan−1 (a/g), the string again makes the same angle with the normal to the ceiling. Can a person sitting inside the compartment tell by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline? If yes, how? If not, then suggest a method to do so.
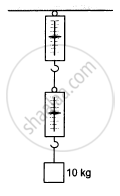
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
What do you mean by inertia of motion?
What do you mean by inertia of rest?
Differentiate between gravitational mass and inertial mass.
Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2 m, respectively, are held at rest such that the spring is in natural length. Find out the accelerations of both the blocks just after release.

