Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A plumb bob is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. If the train moves with an acceleration 'a' along a straight horizontal track , the string supporting the bob makes an angle tan−1 (a/g) with the normal to the ceiling. Suppose the train moves on an inclined straight track with uniform velocity. If the angle of incline is tan−1 (a/g), the string again makes the same angle with the normal to the ceiling. Can a person sitting inside the compartment tell by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline? If yes, how? If not, then suggest a method to do so.
उत्तर
No, a person sitting inside the compartment can't tell just by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline.
When the train is accelerating along the horizontal, the tension in the string is \[m\sqrt{g^2 + a^2}\] when it is moving on the inclined plane, the tension is mg. So, by measuring the tension in the string we can differentiate between the two cases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a carpet is beaten with a stick, dust comes out of it. Explain.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Newton’s first law of motion is also called Galileo’s law of ………………………
A moving bicycle comes to rest after sometime if we stop pedalling it. But Newton’s first law of motion says that a moving body should continue to move for ever, unless some external force acts on it. How do you explain the bicycle case ?
The acceleration of a particle is zero, as measured from an inertial frame of reference. Can we conclude that no force acts on the particle?
Consider a book lying on a table. The weight of the book and the normal force by the table in the book are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Is this an example of Newton's third law?
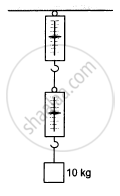
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 m/s on a frictionless horizontal table. The force required to keep this object moving with the same velocity is :
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
A force of 600 dynes acts on a glass ball of mass 200 g for 12 s. If initially, the ball is at rest, find
- Final velocity
- Distance covered.
What do you mean by inertia of motion?
The amount of inertia of a body depends on its _________.
Classify the types of force based on their application.
A mass of 2 kg is suspended with thread AB (Figure). Thread CD of the same type is attached to the other end of 2 kg mass. Lower thread is pulled gradually, harder and harder in the downward directon so as to apply force on AB. Which of the threads will break and why?

Block A of weight 100 N rests on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle 30° (figure). A flexible cord attached to A passes over a frictonless pulley and is connected to block B of weight W. Find the weight W for which the system is in equilibrium.

A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2 m, respectively, are held at rest such that the spring is in natural length. Find out the accelerations of both the blocks just after release.

A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
