Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a train starts, the head of a standing passenger seems to be pushed backward. Analyse the situation from the ground frame. Does it really go backward? Coming back to the train frame, how do you explain the backward movement of the head on the basis of Newton's laws?
उत्तर
No, w.r.t. the ground frame, the person's head is not really pushed backward.
As the train moves, the lower portion of the passenger's body starts moving with the train, but the upper portion tries to be in rest according to Newton's first law and hence, the passenger seems to be pushed backward.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman hits a cricket ball which then rolls on a level ground. After covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest. The ball slows to a stop because ______.
A moving bicycle comes to rest after sometime if we stop pedalling it. But Newton’s first law of motion says that a moving body should continue to move for ever, unless some external force acts on it. How do you explain the bicycle case ?
Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle?
It is sometimes heard that the inertial frame of reference is only an ideal concept and no such inertial frame actually exists. Comment.
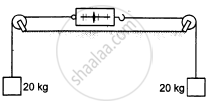
The figure shows a light spring balance connected to two blocks of mass 20 kg each. The graduations in the balance measure the tension in the spring. (a) What is the reading of the balance? (b) Will the reading change if the balance is heavy, say 2.0 kg? (c) What will happen if the spring is light but the blocks have unequal masses?
Three rigid rods are joined to form an equilateral triangle ABC of side 1 m. Three particles carrying charges 20 μC each are attached to the vertices of the triangle. The whole system is at rest in an inertial frame. The magnitude of the resultant force on the charged particle at A is.
A particle stays at rest as seen in a frame. We can conclude that
(a) the frame is inertial
(b) resultant force on the particle is zero
(c) the frame may be inertial but the resultant force on the particle is zero
(d) the frame may be non-inertial but there is a non-zero resultant force
The force exerted by the floor of an elevator on the foot of a person is more than the weight of the person if the elevator is
(a) going up and slowing down
(b) going up and speeding up
(c) going down and slowing down
(d) going down and speeding up
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 m/s on a frictionless horizontal table. The force required to keep this object moving with the same velocity is :
State Newton's first law of motion.
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
A man riding on a car has ___________ Inertia.
What do you mean by inertia of rest?
Name the scientist who first stated the law of inertia.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
In the above given problem if the lower thread is pulled with a jerk, what happens?
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

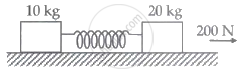
The masses of 10 kg and 20 kg, respectively, are connected by massless spring as shown in the figure. A force of 200 N acts on the 20 kg mass. At the instant shown, the 10 kg mass has acceleration of 12 m/s2. What is the acceleration of 20 kg mass?
(g = 10 m/s2)