Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a train starts, the head of a standing passenger seems to be pushed backward. Analyse the situation from the ground frame. Does it really go backward? Coming back to the train frame, how do you explain the backward movement of the head on the basis of Newton's laws?
उत्तर
No, w.r.t. the ground frame, the person's head is not really pushed backward.
As the train moves, the lower portion of the passenger's body starts moving with the train, but the upper portion tries to be in rest according to Newton's first law and hence, the passenger seems to be pushed backward.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a carpet is beaten with a stick, dust comes out of it. Explain.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Newton’s first law of motion is also called Galileo’s law of ………………………
Find the acceleration produced by a force of 5 N acting on a mass of 10 kg.
Name the law involved in the following situation :
if there were no friction and no air resistance, then a moving bicycle would go on moving for ever.
Is it possible for a particle to describe a curved path if no force acts on it? Does your answer depend on the frame of reference chosen to view the particle?
Neglect the effect of rotation of the earth. Suppose the earth suddenly stops attracting objects placed near its surface. A person standing on the surface of the earth will.
The force exerted by the floor of an elevator on the foot of a person is more than the weight of the person if the elevator is
(a) going up and slowing down
(b) going up and speeding up
(c) going down and slowing down
(d) going down and speeding up
A particle is observed from two frames S1 and S2. Frame S2 moves with respect to S1with an acceleration a. Let F1 and F2 be the pseudo forces on the particle when seen from S1 and S2, respectively. Which of the following is not possible?
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
Explain the following :
After alighting from a moving bus , one has to run for some distance in the direction of bus in order to avoid falling .
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
A force of 600 dynes acts on a glass ball of mass 200 g for 12 s. If initially, the ball is at rest, find
- Final velocity
- Distance covered.
The greater is the __________ the greater is the inertia of an object.
Differentiate between gravitational mass and inertial mass.
If a 5 N and a 15 N forces are acting opposite to one another. Find the resultant force and the direction of action of the resultant force.
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6 N and 8 N. The resultant acceleration of the body is ______.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(4/3)` w.r.t 6 N force.
- 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
- 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan−1 `(3/4)` w.r.t 8 N force.
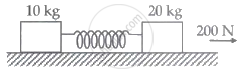
The masses of 10 kg and 20 kg, respectively, are connected by massless spring as shown in the figure. A force of 200 N acts on the 20 kg mass. At the instant shown, the 10 kg mass has acceleration of 12 m/s2. What is the acceleration of 20 kg mass?
(g = 10 m/s2)
This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
Statement 1: If you push on a cart being pulled by a horse so that it does not move, the cart pushes you back with an equal and opposite force.
Statement 2: The cart does not move because the force described in statement 1 cancel each other.
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Newton’s I law | propulsion of a rocket |
| b. Newton’s II law | Stable equilibrium of the body |
| c. Newton’s III law | Law of force |
| d. Law of conservation of Linear momentum | Flying nature of bird |
