Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
उत्तर
Statement of Newton's first law: If a body is in a state of rest, it will remain in the state of rest, and if the body is in the state of motion, it will remain moving in the same direction with the same speed unless an external force is applied on it.
Explanation: Newton's first law can be explained in the following two parts:
(i) Definition of inertia: The 1st part of Newton's first law of motion gives the definition of inertia, according to which an object cannot change its state by itself.
Example: A book lying on a table will remain in its position unless it is displaced.
(ii) Definition of force: The 2nd part of Newton's first law defines force, according to which force is that external cause which can move a stationary object or which can stop a moving object.
Example: A book lying on a table is displaced from its place when it is pushed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A batsman hits a cricket ball which then rolls on a level ground. After covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest. The ball slows to a stop because ______.
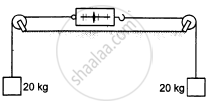
The figure shows a light spring balance connected to two blocks of mass 20 kg each. The graduations in the balance measure the tension in the spring. (a) What is the reading of the balance? (b) Will the reading change if the balance is heavy, say 2.0 kg? (c) What will happen if the spring is light but the blocks have unequal masses?
Consider a book lying on a table. The weight of the book and the normal force by the table in the book are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Is this an example of Newton's third law?
A plumb bob is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. If the train moves with an acceleration 'a' along a straight horizontal track , the string supporting the bob makes an angle tan−1 (a/g) with the normal to the ceiling. Suppose the train moves on an inclined straight track with uniform velocity. If the angle of incline is tan−1 (a/g), the string again makes the same angle with the normal to the ceiling. Can a person sitting inside the compartment tell by looking at the plumb line whether the train is accelerating on a horizontal straight track or moving on an incline? If yes, how? If not, then suggest a method to do so.
A block of mass 2 kg placed on a long frictionless horizontal table is pulled horizontally by a constant force F. It is found to move 10 m in the first seconds. Find the magnitude of F.
The greater is the __________ the greater is the inertia of an object.
What do you mean by inertia of rest?
Classify the types of force based on their application.
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

