Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State and explain the law of inertia (or Newton's first law of motion).
उत्तर
Statement of Newton's first law: If a body is in a state of rest, it will remain in the state of rest, and if the body is in the state of motion, it will remain moving in the same direction with the same speed unless an external force is applied on it.
Explanation: Newton's first law can be explained in the following two parts:
(i) Definition of inertia: The 1st part of Newton's first law of motion gives the definition of inertia, according to which an object cannot change its state by itself.
Example: A book lying on a table will remain in its position unless it is displaced.
(ii) Definition of force: The 2nd part of Newton's first law defines force, according to which force is that external cause which can move a stationary object or which can stop a moving object.
Example: A book lying on a table is displaced from its place when it is pushed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the other name of Newton’s first law of motion ?
Name the scientist who gave the laws of motion.
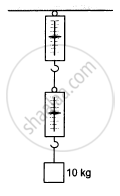
A block of mass 10 kg is suspended from two light spring balances, as shown in the following figure.
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
A force of 600 dynes acts on a glass ball of mass 200 g for 12 s. If initially, the ball is at rest, find
- Final velocity
- Distance covered.
The greater is the __________ the greater is the inertia of an object.
Name the different kinds of inertia an object can possess. Give an example of each.
Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2 m, respectively, are held at rest such that the spring is in natural length. Find out the accelerations of both the blocks just after release.

A force F is applied to the initially stationary cart. The variation of force with time is shown in the figure. The speed of the cart at t = 5 sec is ______.

A balloon has mass of 10 g in air. The air escapes from the balloon at a uniform rate with velocity 4.5 cm/s. If the balloon shrinks in 5 s completely. Then, the average force acting on that balloon will be (in dyne).
