Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a book lying on a table. The weight of the book and the normal force by the table in the book are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Is this an example of Newton's third law?
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a carpet is beaten with a stick, dust comes out of it. Explain.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed.
What is the other name of Newton’s first law of motion ?
State Newton’s first law of motion. Give two examples to illustrate Newton’s first law of motion.
Name the law involved in the following situation :
if there were no friction and no air resistance, then a moving bicycle would go on moving for ever.
It is sometimes heard that the inertial frame of reference is only an ideal concept and no such inertial frame actually exists. Comment.
A block of 2 kg is suspended from a ceiling by a massless spring of spring constant k = 100 N/m. What is the elongation of the spring? If another 1 kg is added to the block, what would be the further elongation?
'When a hanging carpet is beaten with a stick, the dust particles start coming out of it'. This phenomenon can be best explained by making use of :
Give qualitative definition of force on the basic of Newton's first law of motion.
How does Newton's second law of motion differ from the first law of motion?
What do you mean by inertia of motion?
Give one example each of inertia of rest and inertia of motion.
A man riding on a car has ___________ Inertia.
Differentiate between gravitational mass and inertial mass.
If a 5 N and a 15 N forces are acting opposite to one another. Find the resultant force and the direction of action of the resultant force.
A smooth sphere of radius R and mass M is placed on the smooth horizontal floor. Another smooth particle of mass m is placed on the sphere and a horizontal force F is applied on the sphere as shown. If the particle does not slip on the sphere then the value of force F is ______.

Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2 m, respectively, are held at rest such that the spring is in natural length. Find out the accelerations of both the blocks just after release.

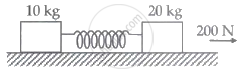
The masses of 10 kg and 20 kg, respectively, are connected by massless spring as shown in the figure. A force of 200 N acts on the 20 kg mass. At the instant shown, the 10 kg mass has acceleration of 12 m/s2. What is the acceleration of 20 kg mass?
(g = 10 m/s2)