Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A block A can slide on a frictionless incline of angle θ and length l, kept inside an elevator going up with uniform velocity v in the following figure. Find the time taken by the block to slide down the length of the incline if it is released from the top of the incline.
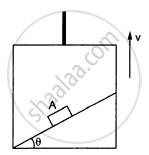
Solution
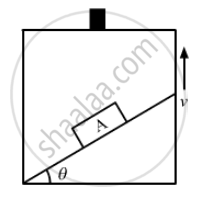
The force on the block which makes the body move down the plane is the component of its weight parallel to the inclined surface.
F = mg sinθ
Acceleration, g = sin θ
Initial velocity of block, u = 0
Distance to be covered
s = l
a = g sin θ
Using, \[s = ut + \frac{1}{2}a t^2\]
\[l = 0 + \frac{1}{2}\left( g\sin\theta \right) t^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow t^2 = \frac{2l}{g\sin\theta}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text{ Time taken }, t ={\sqrt{\frac{2l}{gsin\theta}}}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A rocket with a lift-off mass 20,000 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 5.0 m s–2. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast.
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 15°. What is the radius of the loop?
An object is placed far away from all the objects that can exert force on it. A frame of reference is constructed by taking the origin and axes fixed in this object. Will the frame be necessarily inertial?
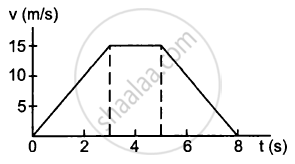
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
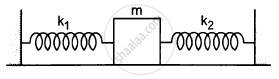
Both the springs shown in the following figure are unstretched. If the block is displaced by a distance x and released, what will be the initial acceleration?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
In the following figure, m1 = 5 kg, m2 = 2 kg and F = 1 N. Find the acceleration of either block. Describe the motion of m1 if the string breaks but F continues to act.
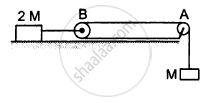
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
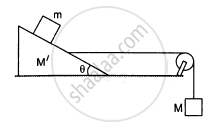
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
A tennis ball and a cricket ball , both are stationary. To start motion in them .
The correct form of Newton's second law is :
The unit of linear momentum is :
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50 g is 0.5 kg m s-1. Find its velocity.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity 30 ms-1. It is stopped in 2 s by applying a force of 1500 N through its brakes. Calculate the following values : The change in momentum of car.
Calculate the velocity of a body of mass 0.5 kg, when it has a linear momentum of 5 Ns.
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
ame the law of motion which gives the definition of force.
Which of the following has the largest inertia?
What do you mean by linear momentum of a body? A force causes an acceleration of 10 ms-2 in a body of mass 1 kg. What acceleration will be caused by the same force in a body of mass 4 kg?
