Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
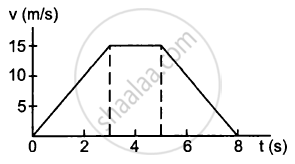
A particle of mass 50 g moves in a straight line. The variation of speed with time is shown in the following figure. Find the force acting on the particle at t = 2, 4 and 6 seconds.
Solution
Given:
Mass of the particle, m = 50 g = 5 × 10−2 kg
Slope of the v-t graph gives acceleration.
At t = 2 s,
Slope = \[\frac{15}{3} = 5 m/ s^2\]
So, acceleration, a = 5 m/s2
F = ma = 5 × 10−2 × 5
⇒ F = 0.25 N along the motion.
At t = 4 s,
Slope = 0
So, acceleration, a = 0
⇒ F = 0
At t = 6 sec,
Slope =\[\frac{- 15}{3} = - 5 m/ s^2\]
So, acceleration, a = − 5 m/s2
F = ma = − 5 × 10−2 × 5
⇒ F = − 0.25 N along the motion
or, F = 0.25 N opposite the motion.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 45° without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
A force \[\vec{F} = \vec{v} \times \vec{A}\] is exerted on a particle in addition to the force of gravity, where \[\vec{v}\] is the velocity of the particle and \[\vec{A}\] is a constant vector in the horizontal direction. With what minimum speed, a particle of mass m be projected so that it continues to move without being defelected and with a constant velocity?
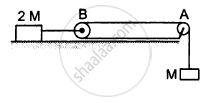
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. (a) Find the acceleration of the mass M; (b) find the tension in the string; (c) calculate the force exerted by the clamp on the pulley A in the figure.
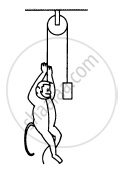
A monkey is climbing on a rope that goes over a smooth light pulley and supports a block of equal mass at the other end in the following figure. Show that whatever force the monkey exerts on the rope, the monkey and the block move in the same direction with equal acceleration. If initially both were at rest, their separation will not change as time passes.
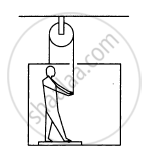
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The impulse of a body is equal to:
Name the physical entity used for quantifying the motion of a body.
Why is it advantageous to turn before taking a long jump?
State Newton's second law of motion.
A body of mass 400 g is resting on a frictionless table. Find the acceleration of the body when acted upon by a force of 0.02 N.
A ball is thrown vertically downward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. What is its speed 1 s later and 2 s later?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is ______.
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is ______.
Figure shows (x, t), (y, t ) diagram of a particle moving in 2-dimensions.
|
|
 (b) |
If the particle has a mass of 500 g, find the force (direction and magnitude) acting on the particle.

