Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two blocks of equal mass m are tied to each other through a light string. One of the blocks is pulled along the line joining them with a constant force F. Find the tension in the string joining the blocks.
Solution
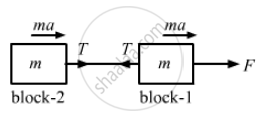
Let a be the common acceleration of the blocks.
For block 1,
For block 2,
T = ma ...(2)
Subtracting equation (2) from (1), we get:
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical circle of radius R. The net forces at the lowest and highest points of the circle directed vertically downwards are: [Choose the correct alternative]
| Lowest Point | Highest Point | |
| a) | mg – T1 | mg + T2 |
| b) | mg + T1 | mg – T2 |
| c) | `mg + T1 –(m_v_1^2)/R` | mg – T2 + ( |
| d) | `mg – T1 – (mv)/R` | mg + T2 + (mv_1^2)/R |
T1 and v1 denote the tension and speed at the lowest point. T2 and v2 denote corresponding values at the highest point.
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by.
Two objects A and B are thrown upward simultaneously with the same speed. The mass of A is greater than that of B. Suppose the air exerts a constant and equal force of resistance on the two bodies.
A smooth wedge A is fitted in a chamber hanging from a fixed ceiling near the earth's surface. A block B placed at the top of the wedge takes time T to slide down the length of the wedge. If the block is placed at the top of the wedge and the cable supporting the chamber is broken at the same instant, the block will.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

Suppose the ceiling in the previous problem is that of an elevator which is going up with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. Find the elongation.
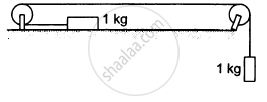
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
An athlete prefers to land on sand instead of hard floor while taking a high jump .
Calculate the magnitude of force which when applied on a body of mass 0.5 kg produces an acceleration of 5 m s-2.
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
A stone is dropped freely from the top of a tower and it reaches the ground in 4 s. Taking g = 10m s-2, calculate the height of the tower.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The time when echo is heard after the pebble is dropped.
A body of mass 200 g is moving with a velocity of 5 ms−1. If the velocity of the body changes to 17 ms−1, calculate the change in linear momentum of the body.
A motorcycle of mass 100 kg is running at 10 ms−1. If its engine develops an extra linear momentum of 2000 Ns, calculate the new velocity of a motorcycle.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
The INCORRECT statement about Newton's second law of motion is
