Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Solution
The free-body diagram of the system is shown below: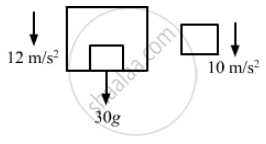
The two bodies are separated because the elevator is moving downward with an acceleration of 12 m/s2 (>g) and the body moves with acceleration, g = 10 m/s2 [Freely falling body]
Now, for the block:
g = 10 m/s2, u = 0, t = 0.2 s
So, the distance travelled by the block is given by
\[s = ut + \frac{1}{2}a t^2 \]
\[ = 0 + \frac{1}{2}10 \times \left( 0 . 2 \right)^2 = 5 \times 0 . 04\]
= 0 . 2 m = 20 cm
The displacement of the body is 20 cm during the first 0.2 s.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A man of mass 70 kg stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving
- upwards with a uniform speed of 10 m s-1
- downwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2
- upwards with a uniform acceleration of 5 m s–2. What would be the readings on the scale in each case?
- What would be the reading if the lift mechanism failed and it hurtled down freely under gravity?
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 m s–2. The crew and the passengers weigh 300 kg. Give the magnitude and direction of the
(a) force on the floor by the crew and passengers,
(b) action of the rotor of the helicopter on the surrounding air,
(c) force on the helicopter due to the surrounding air.
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 15°. What is the radius of the loop?
The rear side of a truck is open and a box of 40 kg mass is placed 5 m away from the open end as shown in Figure. The coefficient of friction between the box and the surface below it is 0.15. On a straight road, the truck starts from rest and accelerates with 2 m s–2. At what distance from the starting point does the box fall off the truck? (Ignore the size of the box).

A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination θ. The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block has a magnitude.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = −kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point x = 20 cm?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
In the previous problem, suppose m2 = 2.0 kg and m3 = 3.0 kg. What should be the mass m, so that it remains at rest?
Find the acceleration of the 500 g block in the following figure.
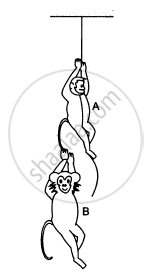
A monkey of mass 15 kg is climbing a rope fixed to a ceiling. If it wishes to go up with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, how much force should it apply on the rope? If the rope is 5 m long and the monkey starts from rest, how much time will it take to reach the ceiling?
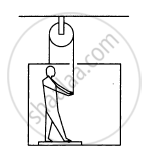
In the following figure shows a man of mass 60 kg standing on a light weighing machine kept in a box of mass 30 kg. The box is hanging from a pulley fixed to the ceiling by a light rope, the other end of which is held by the man himself. If the man manages to keep the box at rest, what is the weight recorded on the machine? What force should he exert on the rope to record his correct weight on the machine?
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : Change in momentum of the body.
Prove mathematically F = ma
A stone is dropped from a cliff 98 m high.
What will be its speed when it strikes the ground?
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 9.8 m/s. When will it reach the ground?
A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies ______.
