Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
Solution
Air applies a velocity-dependent force on the parachute in upward direction when the parachute opens. This force opposes the gravitational force acting on the spy. Hence, the net force in the downward direction decreases and the spy decelerates.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A constant retarding force of 50 N is applied to a body of mass 20 kg moving initially with a speed of 15 ms–1. How long does the body take to stop?
A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical circle of radius R. The net forces at the lowest and highest points of the circle directed vertically downwards are: [Choose the correct alternative]
| Lowest Point | Highest Point | |
| a) | mg – T1 | mg + T2 |
| b) | mg + T1 | mg – T2 |
| c) | `mg + T1 –(m_v_1^2)/R` | mg – T2 + (`mv_1^2`)/R |
| d) | `mg – T1 – (mv)/R` | mg + T2 + (mv_1^2)/R |
T1 and v1 denote the tension and speed at the lowest point. T2 and v2 denote corresponding values at the highest point.
A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
A person drops a coin. Describe the path of the coin as seen by the person if he is in (a) a car moving at constant velocity and (b) in a free falling elevator.
car moving at 40 km/hr is to be stopped by applying brakes in the next 4 m. If the car weighs 2000 kg, what average force must be applied to stop it?
Find the reading of the spring balance shown in the following figure. The elevator is going up with an acceleration g/10, the pulley and the string are light and the pulley is smooth.

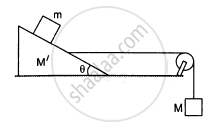
Find the mass M of the hanging block in the following figure that will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are frictionless and the strings and the pulleys are light.
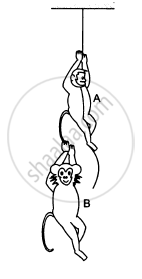
The monkey B, shown in the following figure, is holding on to the tail of monkey A that is climbing up a rope. The masses of monkeys A and B are 5 kg and 2 kg, respectively. If A can tolerate a tension of 30 N in its tail, what force should it apply on the rope in order to carry monkey B with it? Take g = 10 m/s2.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
Show that the rate of change of momentum = mass × acceleration. Under what condition does this relation hold?
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 3 s, initially at rest. Calculate : The velocity acquired by the body
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It returns 6 s later. Calculate : The greatest height reached by the ball . (Take g = 10 m s-2)
An electron of mass 9 × 10−31 kg is moving with a linear velocity of 6 × 107 ms−1. Calculate the linear momentum of electron.
What do you understand by the term momentum?
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
A force acts on a body of mass 3 kg such that its velocity changes from 4 ms−1 to 10 ms−1. The change in momentum of the body is
What do you mean by an impulsive force?
A ball is thrown vertically downward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. What is its speed 1 s later and 2 s later?
A stone is dropped from a tower 98 m high. With what speed should a second stone be thrown 1 s later so that both hit the ground at the same time?
A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t) = pt + qt2 + rt3 where p = 3 ms−1, q = 4 ms−2 and r = 5 ms−3. The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is ______.
