Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A spy jumps from an airplane with his parachute. The spy accelerates downward for some time when the parachute opens. The acceleration is suddenly checked and the spy slowly falls to the ground. Explain the action of the parachute in checking the acceleration.
उत्तर
Air applies a velocity-dependent force on the parachute in upward direction when the parachute opens. This force opposes the gravitational force acting on the spy. Hence, the net force in the downward direction decreases and the spy decelerates.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body of mass 0.40 kg moving initially with a constant speed of 10 m s–1 to the north is subject to a constant force of 8.0 N directed towards the south for 30 s. Take the instant the force is applied to be t = 0, the position of the body at that time to be x = 0, and predict its position at t = –5 s, 25 s, 100 s.
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F = 600 N is applied to
- A,
- B along the direction of string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
Explain why a cricketer moves his hands backwards while holding a catch.
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope in given Figure which can stand a maximum tension of 600 N. In which of the following cases will the rope break: the monkey
(a) climbs up with an acceleration of 6 m s–2
(b) climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m s–2
(c) climbs up with a uniform speed of 5 m s–1
(d) falls down the rope nearly freely under gravity?
(Ignore the mass of the rope).

A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the trolley is 0.18. The trolley accelerates from rest with 0.5 ms–2 for 20 s and then moves with uniform velocity. Discuss the motion of the block as viewed by (a) a stationary observer on the ground, (b) an observer moving with the trolley.
The force of buoyancy exerted by the atmosphere on a balloon is B in the upward direction and remains constant. The force of air resistance on the balloon acts opposite the direction of velocity and is proportional to it. The balloon carries a mass M and is found to fall to the earth's surface with a constant velocity v. How much mass should be removed from the balloon so that it may rise with a constant velocity v?
An empty plastic box of mass m is found to accelerate up at the rate of g/6 when placed deep inside water. How much sand should be put inside the box so that it may accelerate down at the rate of g/6?
In the following figure shows a uniform rod of length 30 cm and mass 3.0 kg. The strings shown in the figure are pulled by constant forces of 20 N and 32 N. Find the force exerted by the 20 cm part of the rod on the 10 cm part. All the surfaces are smooth and the strings and the pulleys are light.

Consider the situation shown in the following figure All the surfaces are frictionless and the string and the pulley are light. Find the magnitude of acceleration of the two blocks.

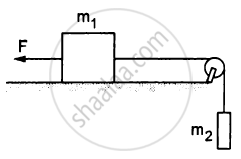
A constant force F = m2g/2 is applied on the block of mass m1 as shown in the following figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of m1.
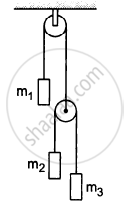
Let m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 2 kg and m3 = 3 kg in the following figure. Find the accelerations of m1, m2 and m3. The string from the upper pulley to m1 is 20 cm when the system is released from rest. How long will it take before m1 strikes the pulley?
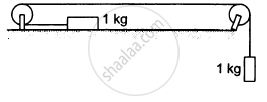
Calculate the tension in the string shown in the following figure. The pulley and the string are light and all the surfaces are frictionless. Take g = 10 m/s2.
An aeroplane is moving uniformly at a constant height under the action of two forces (i) Upward force (lift) and (ii) Downward force (weight). What is the net force on the aeroplane?
State Newton's second law of motion. Under what condition does it take the form F = ma?
Use Newton's second law of motion to explain the following instance :
A cricketer pulls his hands back while catching a fast moving cricket ball .
A force acts for 10 s on a stationary body of mass 100 kg, after which the force ceases to act. The body moves through a distance of 100 m in the next 5 s. Calculate: The velocity acquired by the body.
A pebble is dropped freely in a well from its top. It takes 20 s for the pebble to reach the water surface in the well. Taking g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 330 m s-1. Find : The depth of water surface
Define Newton’s second law of motion.
Prove mathematically F = ma
